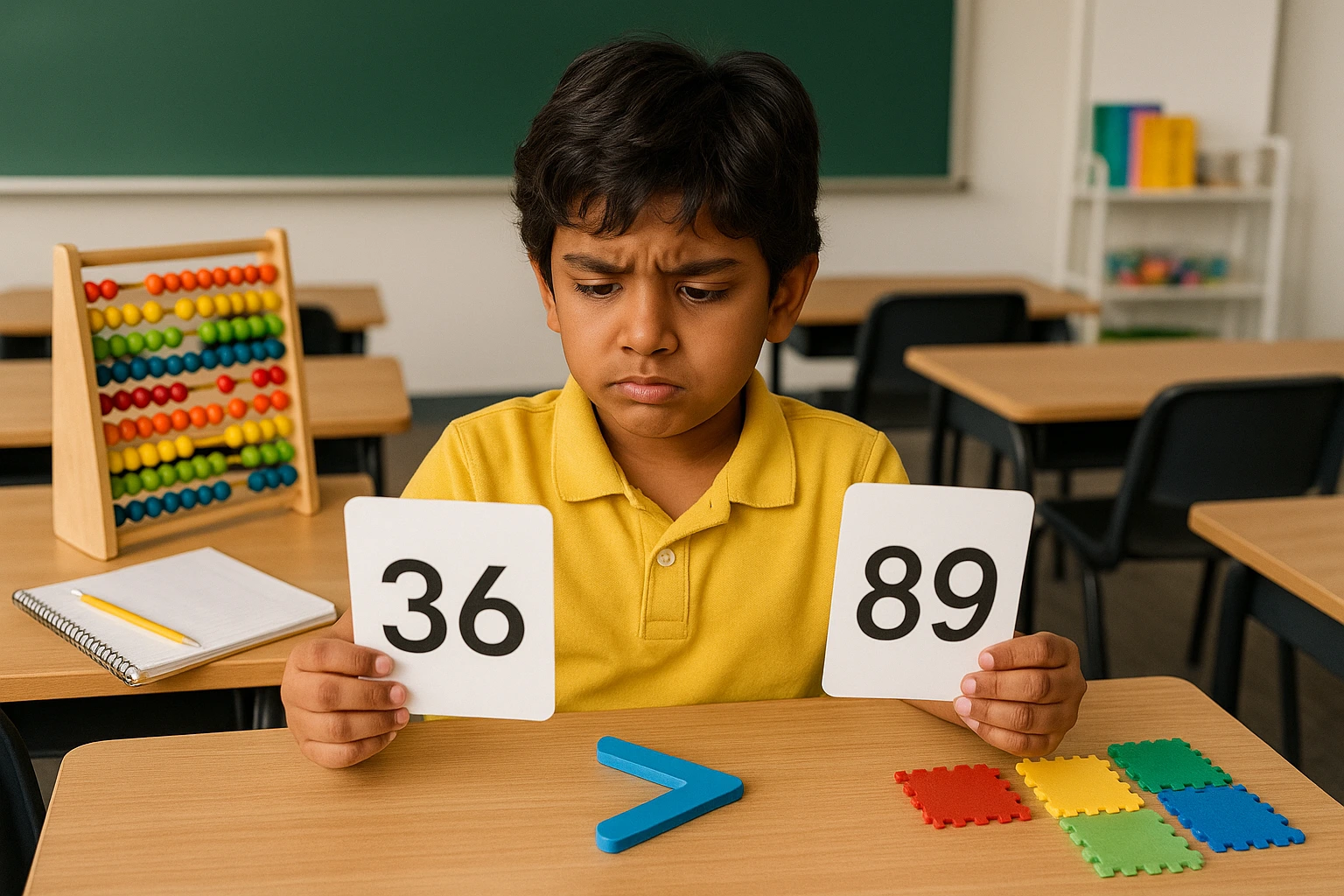

Dyscalculia, a specific learning disorder, hampers the child’s ability to perform basic mathematical operations. It is a disorder that affects the math-related skills only. Children with dyscalculia struggle with understanding number sense, sequencing skills, and the concept of value. Individuals with dyslexia have average intelligence, but their ways of processing concepts, which involve higher-order thinking and arithmetical operations, are affected by certain environmental and genetic factors.
Children with Dyscalculia can gain the desired academic proficiency and confidence in mathematics when they receive the precise academic aid with the help of accurate teaching strategies for dyslexic students.
This article throws light on listing some of the most practical and efficacious instructional techniques that help dyscalculic children enhance their number sense and get rid of their fear of mathematics.
Signs of Dyscalculia
Dyscalculia is a Specific Learning Difficulty identified by a child’s difficulty in understanding and working with numbers. They can experience a disability with math in general. Dyscalculia is certainly more than a difficulty with math; it can show up as a constant sense of confusion and frustration when attempting even the simplest of math tasks. The earlier we can recognize these signs, the better we can support your child.
To Download the Brochure of the LD Course, Click Here!
For more Details of the LD Course, Call / WhatsApp on +919321024137 / +919869866277
Here are common signs of dyscalculia:
Number Sense and Concepts
- Trouble with number recognition: Difficulty in identifying or calling numbers correctly.
- Understanding number sequencing problems: Children do not understand the basics of value, due to which sequencing is a huge issue for them.
- Value understanding issues: Dyslexic children cannot process the concept of value related to the numbers, due to which they cannot understand the concept of ones, tens, hundreds, thousands, etc
- Trouble with quantity and comparison: Trouble when comparing numbers or estimating which is bigger or smaller.
- Trouble understanding the concept of zero: Trouble understanding zero as a placeholder or as an indicator of ‘nothing.’
Math Facts and Calculations
- Struggle to retain information of basic facts: Dyslexic children fail to remember information, especially crucial topics of tables.
- Calculations can be a cause for anxiety: Dyslexic children possess Slow processing speed for calculations, causing anxiety while solving problems.
- Dependence on counting: often uses fingers or visual or tactile tools instead of remembering facts.
- Calculating in mind is a struggle: Children have a problem with doing basic math calculations in their minds, hampering their cognitive abilities.
Problem-Solving and Reasoning
- Difficulty with word problems: Having trouble converting written problems into equations.
- Abstract concepts issues: Children cannot connect with abstract concepts due to which prevents them from performing problems related to abstract concepts.
- Too many steps: Problems that consist of several steps can be difficult for dyslexic children.
- Struggles with spatial reasoning: Dyslexic children find it difficult to judge directions, calculate distances, or understand angles as well,
Other Signs
- Time-related difficulties: Trouble reading clocks or understanding time intervals.
- Issues related to money: Dyslexic children cannot calculate money-related problems or even recognize coin values.
- Emotional struggles: Due to continuous struggles to perform correctly, children may experience frustration that can lead to low self-esteem and poor self-confidence.
When these warning signs are identified, it helps to start the interventions at an early stage, providing the child with the desired academic support.

Source: reviewofoptometry
Strategies to Help with Dyscalculia
To assist dyscalculic students, we need to introduce some research-backed teaching methods that would allow math to be more accessible, visual, and meaningful. Since numbers often feel abstract and confusing for students with dyscalculia, structured, tangible, and meaningful methods are the best way to help students improve their understanding and gain confidence.
Some effective strategies to use to support students with dyscalculia:
Putting thoughts on paper
A lot of children can achieve better outcomes when they put down their thoughts on paper or write what they must solve. When they write down the problem, it helps them connect better with abstract concepts. This helps them to understand abstract concepts well, which can be useful for mapping relationships and solving problems.
Draw the Problem
Drawing connects parts of a problem to create a visual representation for students. Drawing bar models, diagrams, or simple pictures can help them make sense of what they are doing in math and will help make abstract math more concrete.
Complex to simple
Divide the complex problem into easy, manageable steps that help children master simple basic concepts, allowing students to focus well, which ensures less stress and more clarity.
Use Real-Life Cues and Physical Objects
Putting math to everyday situations, such as using coins, clocks, or measuring tools, helps students relate numbers to practical use. Physical use of objects improves understanding and memory.
Review Often
Dyscalculic students benefit from regular reviews, as remembering math concepts can be difficult. Conducting periodic reviews at regular intervals can be extremely helpful for long-term learning.
When a child can relate well to Math, it helps him understand it better without fearing it. Using crucial Teaching Strategies can help dyscalculic children achieve mastery over basic concepts that strengthen their mathematical skills, enabling better academic progress in Math.
Classroom Accommodations for Dyscalculia
Incorporating simple accommodation for students with dyscalculia helps them eradicate barriers to learning and improve their math-related competencies. These accommodations support the child’s learning and help to reinforce core concepts, helping children be comfortable with Mathematics.
Classroom and Homework Modifications
- Use of a Calculator: Helps bypass difficulties with basic operations, allowing focus on problem-solving.
- Reference Sheets: Providing formula charts or multiplication tables supports memory and reduces cognitive load.
- Graphic Organizers: Tools like graph paper or visual templates help organize work and improve clarity.
- Oral Examinations: Some students express understanding better verbally than in written form.
Learning and Presentation Support
- Different modes of learning: Using multi-sensorial modes of learning helps to stimulate the child’s learning skills, which can be useful for retaining the concepts for a longer time.
- Chunking instructions: Breaking down the tasks into small steps can help children understand basic steps with maximum clarity.
- Regular breaks: The child should be provided with periodic breaks to focus better and freshen their minds.
Assessment Accommodations
- More time: A little extra time should be provided so that students are not in a hurry to finish the test, but focus thoughtfully on solving problems.
- Varied forms of getting answers.
- Flexible Response Formats: Using number lines, manipulatives, or oral answers provides alternate ways to show understanding.
Students can require different supports. It is important to individualize the accommodations of learners who are dyscalculic, often based on an educational assessment, to optimize learning.
What Training is Available to Support Dyscalculic Students?
Supporting children with dyscalculia needs in-depth knowledge of dyscalculia and the strategies used for helping children overcome the struggles they are facing. They will benefit greatly from professional development in learning differences. One option is taking a Learning Disability Course that focuses on assisting students with challenges in mathematics and in academics overall.
The thoughtfully curated Learning Disability Course at Vidhyanidhi Education Society (Govt. Regd.) encompasses all the essential aspects of different learning disabilities, helping teachers to create conducive learning classrooms, enhancing the learning outcomes for all children, and helping children with specific learning disorders acquire education in a learning style aligned to their learning methods.
Key highlights of the Learning Disability Course include:
- Gaining basic, valuable, and deep insights into Dyscalculia
- Crucial training on how to devise the most important individualized education plans (IEPs)
- Use of assistive tools and technology to improve learning results.
- Guidance on building student confidence and reducing math-related anxiety.
Vidhyanidhi Education Society (Govt. Regd.), an eminent Teacher Training Institute, has successfully produced countless proficient Special Educators with the help of their top-notch Learning Disability Course. This course, designed under the guidance of leading professionals, has helped trainees acquire deep, valuable insights about various learning disabilities, enabling them to offer the desired academic support to children battling with Learning Disorders.
Transform learning challenges into strengths with Vidhyanidhi’s expert LD course today!
To Download the Brochure of the LD Course, Click Here!
For more Details of the LD Course, Call / WhatsApp on +919321024137 / +919869866277
FAQs
How to Test for Dyscalculia?
Dyscalculia is assessed using cognitive tests, specific math tasks, and standardized assessments that can only be administered by a proper educational psychologist or specialist.
Do Calculators Help with Dyscalculia?
Children with Dyscalculia can be helped tremendously with a calculator, as it drastically reduces their anxiety of calculating, enabling them to focus on solving problems.
What Type of Learning Disability is Dyscalculia?
Dyscalculia is a specific learning disorder that exclusively targets the mathematical skills of the child, leading to poor academic progress.



